Join
Use the Join tool to add another data set to an existing one by appending columns. Match columns based on selected key columns to look up and pull the corresponding data. Ensure at least one common column in both data sets when joining data. The common column is known as a key column.
If you want to add another data set, but restrict it to only matching columns, use the Union tool instead.
Learn more about the join types...
Input and output
To use this tool, you need two data sets.
When you run this tool, it appends columns to the primary data set based on the secondary data set. The data type must be the same in both key columns.
Tip
Ensure you join all appropriate columns in your sources, so you don't get duplicate records.
Configuration
Use the following configuration options to configure the Join tool.
Go to the Pipes module from the side navigation bar.
From the Pipes tab, click an existing pipe to open, or create a new pipe. To create a new pipe, read the Creating a pipe documentation.
In Pipe builder, add your data sources.
Click
 +Add Tool.
+Add Tool.Click See all tools.
In the search bar, search for the Join tool. Click Add tool.
Tip
You can also find the Join tool in the Combine section.
Connect the tools to your data sets.
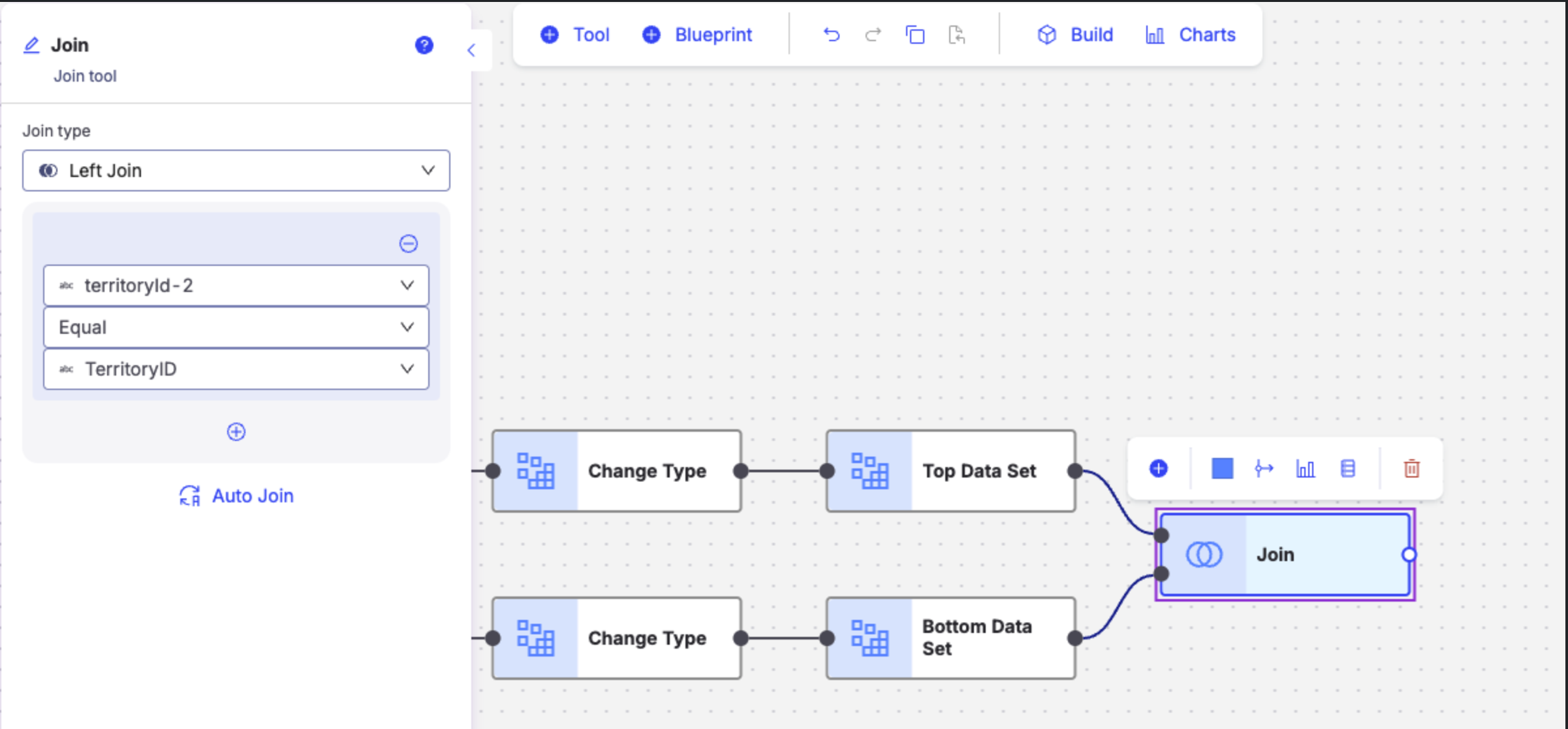
In the configuration pane, under Join conditions, select the join type:
Left join: Values appear in the left data set output when joined, regardless of a match.
Right join: Values appear in the right data set output when joined, regardless of a match.
Inner join: Values must exist and match in both data sets for the results to appear in the output.
Left anti: Values from the left table that don’t have any matching rows from the right table appear in the output.
Full outer: Returns all records in both the top (Left) and bottom (Right) data sets, regardless of match.
Cross join: Returns the Cartesian product of prows from the left and right data set.
Caution
Cross join may create memory performance issues if the data source is too large.We are limiting the Cross join to a maximum of 100 columns and 100 million rows to avoid performance issues.
Tip
The default join for the Join tool is the Inner join. In most instances, users use the Inner join. If you intended the join tool to use anything other than an Inner join, we recommend putting that in the name of the tool to make it clear that you intended to use the join type you selected.
For example, let's say you are joining a Quota by Plan to a Quota Override by Payee, a left join is a good choice. In this case, you would name the tool "Left join to get Quota Overrides".
Select the operators to join the top and bottom columns.
Equalis the default operator. You can choose from the following operators to filter:Note
If you select the
Likeoperator, the pattern type appears.Operator
Operator description
Text
Numeric
Boolean
Dates
Equal
Returns a result if the data is equal to another. If the number is not equal, it does not return a result.
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Less than
Returns a result if the left number is less than the right number. If the right number is greater, it returns no result.
Not supported
Supported
Not supported
Supported
Less than or equal
Returns a result of the number less than or equal to another number.
Not supported
Supported
Not supported
Supported
Greater than
Returns a result if the number is greater than another number.
Not supported
Supported
Not supported
Supported
Greater than or equal
Returns a result if the number is greater than or equal to another number.
Not supported
Supported
Not supported
Supported
Like
Returns a result based on the pattern you select: Starts with , Ends with, or Contains.
Supported
Not supported
Not supported
Not supported
In between
Returns a result based on an inclusive effective start and effective end date.
Not supported
Not supported
Not supported
Supported
Optionally, click on Auto join to automatically join the data sets based on matching column names and column types.
Note
Auto join conditions will be created based on the join type selected and will be automatically added to the Join tool configuration.
Optionally click +Add to add another join condition.
Click on the tool name to rename your tool node to a meaningful name. Name your tools in a way that describes the function, not the object or the data action. For example, use “Look up rate” instead of “Join to rate table”.
Usage example
You have two data sets. The Universe column from the top and bottom data sets are the related columns that will allow us to merge the top and bottom nodes together.
Suggestions
The Join tool gives you a breakdown of your data sources and offers suggestions within the Row viewer to help you merge your data and get the results that you want:
Choose alternative or unique columns: This suggestion shows an overlay over the configuration, showing you what you could change to the selected join columns.
Duplicate rows: This suggestion adds the Unique tool between one or both of the incoming data sources if they have duplicate rows. One more both incoming data sources must have duplicate rows.
Clean tools: This suggestion shows you tools to clean the columns in the join conditions if the join results are blank.
Learn more: This suggestion takes you to the Join tool documentation.